7.3 Cybersecurity and Data Protection
In this part of the chapter, we will look closely at cybersecurity and data protection. Both are very important points to consider when planning the introduction and application of Digital Rehabilitation solutions in your work.
7.3.1 Cybersecurity
First, it is crucial to understand what cyberspace is. Cyberspace consists of three layers. The first layer is the national critical infrastructure, which contributes to the cyber resilience of the nation in question. The second layer consists of the cybersecurity elements of the people, processes, and technologies. The third layer consists of the cyberspace actors, which are citizens, business life and the public sector. Together these three layers ensure the existence of a secure cyber environment [9].
Another way of defining cyber environment is to divide it into five different layers. These are physical layer, syntax layer, semantic layer, service layer and cognitive layer. The physical layer includes all devices (e.g., computers, mobile phones) but also network connections (wired and wireless). Syntax layer is a bit more difficult to understand, but it contains all devices connected to the internet, system control programs and network protocols which ensure errorless functionality. Basic user is usually not able to interact with the syntax layer. Semantic layer is usually connected to “main users” of an institution. It includes information and data sets stored in servers and computers, and different user-administered functions, for instance, printer controls or program/system updates. Service layer is the area where a basic user usually acts. It consists of different kinds of digital services, web-based services that the public or private sector produces as well as information and communication services. The last layer, cognitive layer entails the basic user’s understanding of the digital information context, beliefs and assumptions and awareness of digital environment. So, it is the human factor affecting cyberspace [9].
For the user of Digital Rehabilitation services (e.g. rehabilitation professional, community health worker, client) the most important layer is the semantic layer. It consists of all the services and programs we use when applying Digital Rehabilitation solutions, but also it entails all the information we collect and store about our clients. Of course, all these layers are relevant when we want to provide safe and good quality Digital Rehabilitation services. If any of the layers are weak, the rehabilitation process is vulnerable to cyber threats. These vulnerabilities might be, for instance, inadequate protection of hardware, inadequate security software, weak backup systems, insufficient safety protocols and lack of competence and knowledge.
Cybersecurity is a broad term, an umbrella term. This means that it covers smaller entities, in this case: data security, network security, computer security and information technology security. It is also related to the reliability of different kinds of software and applications, robustness of global networks against maleficent attacks and safety of personal data in those networks. The main idea of cybersecurity is to protect the data, which is found in electronic form. Cybersecurity can be discussed in three different topics, and these are 1) threats, 2) protection and 3) privacy [10,11].
Information security means, by definition, the protection of information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. The aim of information security is to provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability [12]. Confidentiality means that the information in question is not accessible to outsiders, to people or processes who are not supposed to be using it. Integrity on the other hand means that the information is trustworthy, which means that the information is not deliberately tampered with or accidentally modified. Term availability refers to the fact that the information is accessible and usable for the people or processes who are trusted with the right to handle it. Also, the term “quality” is good to be added to the list, when discussing information security in Digital Rehabilitation. Quality refers to the information being correct and not misleading.
When applying Digital Rehabilitation, the fact is that we are using different kinds of technologies, which often are connected to global networks. This means that from ethical and regulations perspective, cybersecurity and information security should be considered. In that case, how does Digital Rehabilitation fit in the big picture?
According to von Solms and van Niekerk [13] we can look at the entity through two-circle Venn-diagram (see Figure 1. below). Cybersecurity and information security are partly overlapping concepts, and in this case Digital Rehabilitation is situated in this overlapping area called “Information and communication technology security”. In practice this means that when a rehabilitation professional is working with a service-user using Digital Rehabilitation solutions (for instance with a client in Occupational Therapy), they are working together in both analog and digital world. The concept of Digital Rehabilitation also encompasses the use of phone calls or SMS-messages and if there is an electronic client record system in use, you are dealing with cybersecurity, even though the therapy itself would be in-person.

Figure 1. Digital Rehabilitation in the context of information- and cybersecurity (Adapted from von Solms and van Niekerk [13]).
In conclusion, cybersecurity is a crucial issue to consider in Digital Rehabilitation, because social and healthcare are very tempting targets for cyberattacks. Sensitive information and personal data are valuable, and for instance, malicious software, such as ransomware is often used to gain financial benefit by threatening to expose this information. Also, in hospital setting, people have even died due to cyberattacks directed to hospital infrastructure.
How can you, as basic user, prepare against cyberattacks when applying Digital Rehabilitation? [adapted from 10,11].
- Physical layer: Keep your gadgets safe, use strong passwords, don’t use open WiFi networks when handling client data or other sensitive information.
- Syntax level: Use only secure connections.
- Semantic layer: Keep your anti-virus software, computer security software and firewalls updated, use automatic backup. Discuss cybersecurity in your organization.
- Service level: Use only services which are reliable and secure, e.g., platforms designed for rehabilitation or health care needs.
- Cognitive level: Be vigilant, be sceptic. Keep your work files on your computer or on a secure cloud server. Don't share your username and password with anyone, not even with your colleague (user credentials are always personal). Learn more about cyberthreats and ask for proper training.
7.3.2 Data protection
Let’s start by defining what data protection is. Data protection is defined to be protection of any information which is related to identified or identifiable information of a living person. This includes names, birthdays, videos and photos, email addresses, and phone numbers. Also, IP addresses and communications content are also subject to data protection. This information is called personal data (see also figure 7.2). The purpose of data protection is to ensure that personal data is processed (that is collected, used, and stored) fairly by both the private and public sectors [16].
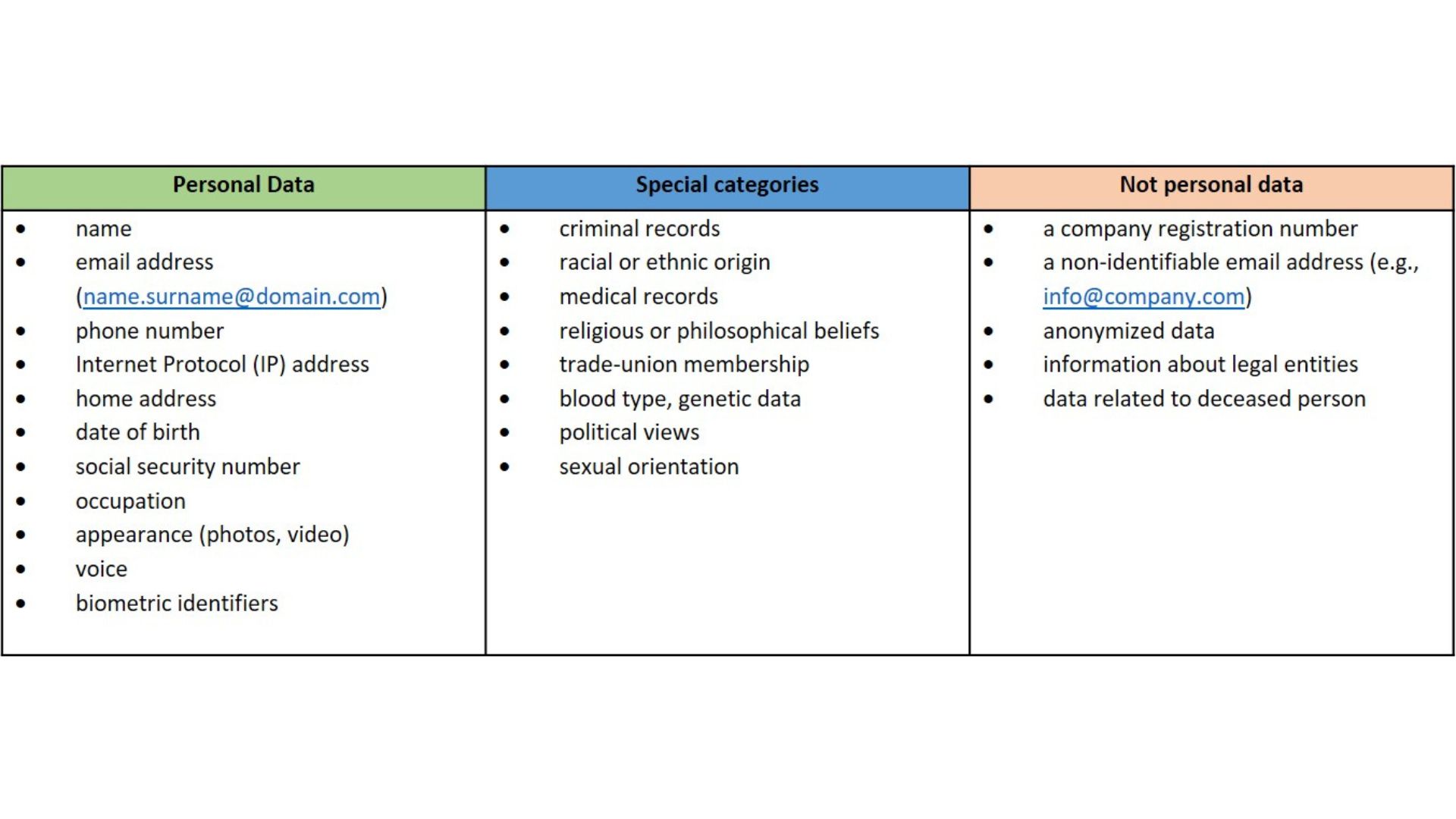
Figure 2. Components of personal data.
The need for data protection arises from people’s right to privacy. Privacy is considered as a universal human right. The right to privacy and private life is embedded in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (Article 12) [17]. Thus, data protection is instrumental in promoting and preserving fundamental rights and values, but also a way to support people in exercising other rights and freedoms, such as the right to assembly.
Data protection is usually ensured via national or international laws. For example, in Europe, the European Union (EU) has had high standards, of the data protection laws for decades and in April 2016 the EU adopted the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which became fully applicable around the globe in May 2018. Even if the GDPR is a European law, it still may affect the people in East Africa. This is because it applies to companies and organizations who offer services or goods to individuals in the EU, or who monitor the behavior of the individuals in the EU area. Few examples from East African community: the Data Protection Act of Kenya came into force in November 2019 (please see https://www.odpc.go.ke/regulatory-framework/ for further information), The Personal Data Protection Act of Tanzania was commenced in June 2023 (please see https://oagmis.agctz.go.tz/portal/acts/237) and Data Protection Law of Rwanda came into effect in October 2021 (for more details, please visit https://www.risa.gov.rw/data-protection-and-privacy-law).
Data protection in social and health care is especially important because of the nature of personal data and is often sensitive due to the characteristics of the disciplines. If this data is accessed without consent it may cause distress, embarrassment, and suffering, but in addition, as discussed before, these kinds of security breaches may lead to financial losses or even decline in physical health and well-being [11,14]. Even though in the field of rehabilitation, the information we gather, and store of the client would not be that sensitive (for instance common knee rehabilitation), still we must remember that it is not only client records that are in threat but the personal identification data. If a maleficent attacker reaches the client database, the clients are exposed to identity thefts, financial loss and psychological suffering.