1.4 Potentials
An important component of universal health coverage (UHC) is to "ensure that all people have access to the necessary health services (including prevention, promotion, treatment, rehabilitation and palliation) in sufficient quantity and quality to be effective, while ensuring that the use of these services does not put the user in financial hardship” [2]. In essence, UHC means that all people everywhere should have access to affordable health services at all times. UHC also implies a strong people-centred health care system based on primary health care. WHO (2020) also emphasizes three interlinked goals:
- Equal opportunities in access to health services - those who need the services should receive them, not just those who can pay for them.
- The quality of healthcare services is good enough to improve the health of those receiving services.
- Protection from financial risk to ensure that the cost of accessing care does not put people in financial hardship
Aiming for UHC for all by 2030 is in line with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.8 [3]. An optimistic point of view for the realization of UHC and global health is the opportunities created by the rapid advances in digital technologies and the spread of mobile networks across the continent.
In the following, we are summarizing the potentials of Digital Rehabilitation from the perspectives of various stakeholders in the system that are relevant for East Africa, see also figure 1. On the one hand, Digital Rehabilitation could have advantages for society and/or the healthcare system as a whole. On the other hand, it has an impact on the client, caregiver and/or the rehabilitation staff. The healthcare provider can also benefit from the implementation of Digital Rehabilitation.
Client: A huge advantage of Digital Rehabilitation is to offer a rehabilitation possibility from a distant to all persons who can’t or do not want to access public rehabilitation and thus does not get the support they need [4]. No access or no possibility of rehabilitation could be due to a lack of health workers, high financial costs associated with rehabilitation, poor transportation possibilities, or geographical distance.
In addition, the lack of privacy in rehabilitation centres and the fear of stigmatization, through the access to healthcare, reduces the utilization of rehabilitation as well. Here, for example, you can think of an app that provides an exercise program for the client to perform at home. Another example is to send therapy reminders via text messaging in order to increase adherence and rehabilitation outcomes.
A further benefit of Digital Rehabilitation is the availability of information even outside the clinical settings. Technologies offer a variety and flexibility for using health information (websites, interactive applications, games, augmented and virtual reality, combinations of text, images, audio and video, social networking tools, animations, risk calculators) that can assist clients matching to their individual needs and preferences.
In addition, use of digital technologies enables individuals to exert more control over one’s health and to have better access to own data, while remaining connected to the healthcare team [5–7]. Some digital tools (for example apps, portable devices with augmented reality) are rather appealing for the clients with entertaining and interactive elements, which capture clients’ attention, engage them cognitively and emotionally. This may lead to increased participation and adherence to the therapy process [8].
Moreover, digital interventions often include peer support networks and online communities where clients can connect with others facing similar challenges. These peer support groups provide a safe space for clients to share their experiences, seek advice, and receive encouragement, reducing feelings of isolation and stigmatization.
Rehabilitation professional: The implementation of Digital Rehabilitation could facilitate the healthcare professional, for example to monitor client’s behaviour, compliance, nutrition, digital health, symptom management, or to undertake quick adaptations of the treatment remotely [9].
Further, digitals solutions have the potential to improve the communication between the client and the healthcare professional, because they enable client-centred and personalized ways of providing information and treatment.
Healthcare provider: Digital technologies could support the management of the healthcare provider by outsourcing processes such as registration and/or billing. Think, for example, of a client who wants to make an appointment at a hospital or practice. The client could register via an online platform and, after adding their personal details, be allocated to an available appointment.
Health care system: Digital Rehabilitation has also the chance to reduce the costs for the client and health care system [10–12] when e.g. face-to-face sessions and travelling to the health care facilities could be reduced.
In addition, some studies showed that Digital Rehabilitation improves outcomes in clients with heart failure, diabetes, and respiratory disease. They also help clients to manage pain, increase their physical activity, and improve mental health, diet quality, and nutrition [13].
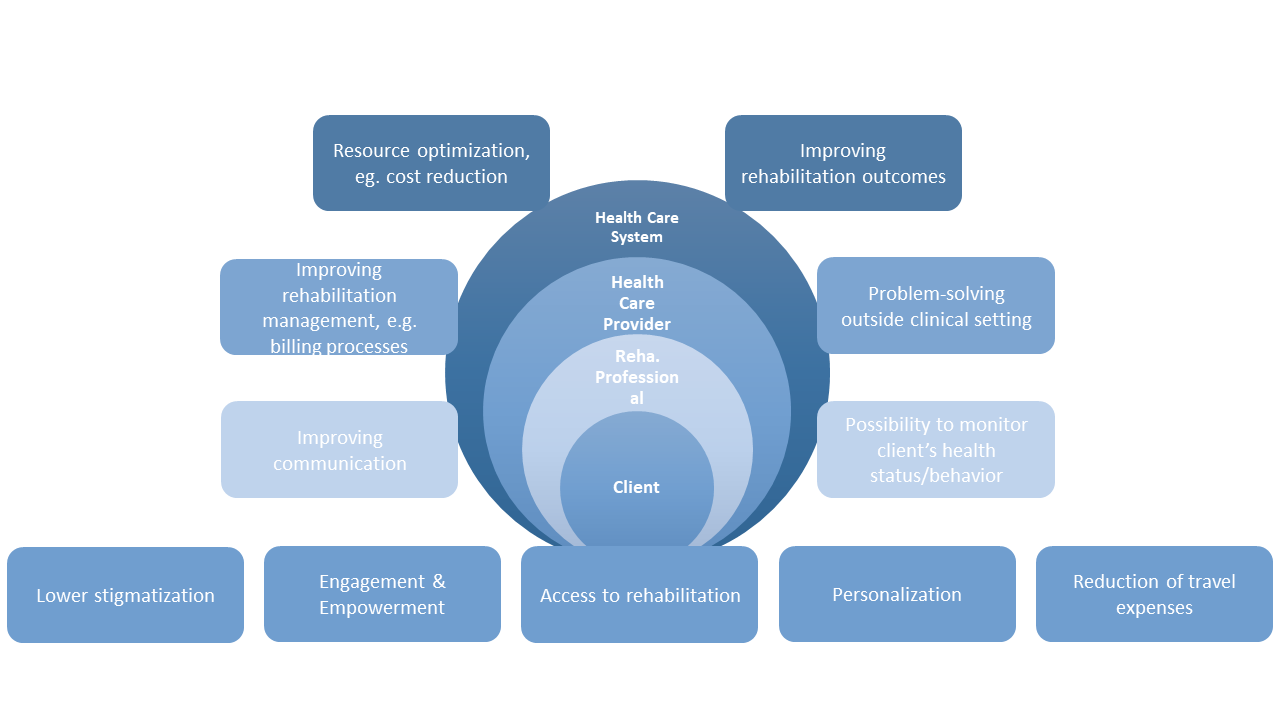
Figure 2. Potential of Digital Rehabilitation per stakeholder.